
We have s,p,d,f atomic orbitals ( AOs ).Įlectrons can be explained via their wave functions in quantum mechanics. An orbital, on the other hand, is defined to be the probability of the presence of an electron in any given regional space.Ītomic orbitals are of several shapes like spherical, dumb-bell, clover-leaf, or doughnut to name a few of the complex varieties. In chemistry, an orbit is a fixed path around the nucleus in which electrons tend to move or revolve. The bond angle is around 103 degrees (due to the repulsion of the lone pair). According to the above chart, we have a bent molecule structure. The VSEPR notation for the OF2 molecule is AX2E2. of lone pairs of electrons of the central atom, ‘X = 2. of surrounding atoms, ‘n’ = 2 ( Fluorine )Į: no.
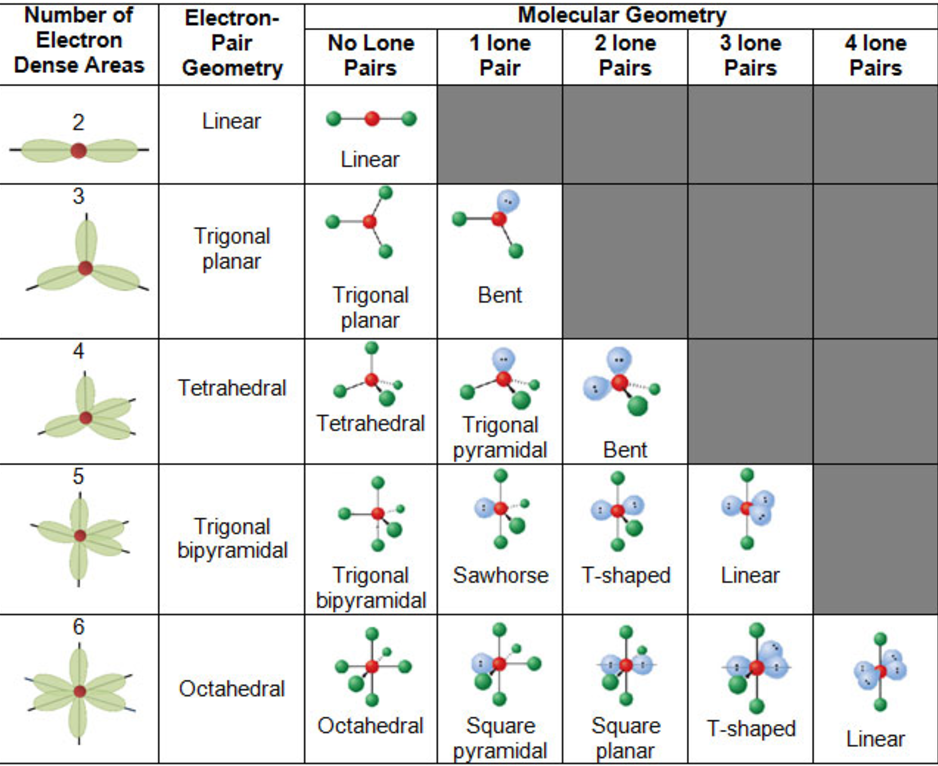
Let us look at this VSEPR chart showing AXN notations:Īccording to AXnEx notation of VSEPR theory, The VSEPR model tends to reduce or minimize the repulsive forces and balance the stability of any given molecule, in this case, OF2. Like charged electrons create a negatively charged cloud surrounding the atomic nuclei and repulsion is created. Our next step is to use Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) to find the exact molecular geometry along with the bond angles. Via Lewis Structure, we have realized the type of bond formed and the number of lone or unbonded pairs of valence electrons present in an OF2 molecule. Now, we are going to decipher the 3D molecular shape. We have already found the 2D Lewis Structure diagram of the Oxygen Difluoride molecule. Here, oxygen forms a single bond with each of the fluorine atoms (O-F). Since the elements are present in their least possible formal charge values, we have achieved our suitable Lewis Structure configuration.

The same goes for the central oxygen atom.īefore we proceed to confirm any sketch to be the perfect Lewis Structure for a given molecule or ionic structure, we need to check the formal charge values.įor Oxygen: Formal Charge = 6 – 0.5*4 – 4 = 6 – 2 – 4 = 0.įor each Fluorine atom: Formal Charge = 7 – 0.5*2 – 6 = 7 – 1 -6 = 0. Here, if we look at the octet rule, both the fluorine atoms have achieved a valency of eight. This is known as octet fulfillment since the elements want to achieve eight electrons in their valence shells.įor example, Carbon tends to attain a Neon configuration.Įxception: Hydrogen tends to achieve Helium configuration, hence only two electrons in the outer shell. The main group elements ( group 1 to group 17 ) of the periodic table have a tendency to attain the octet configuration of the noble gas elements present in group 18 of the same period. Atomic symbols along with dot notations:.Let us look at the below skeletal sketch: In Lewis Structure, we use atomic symbols like C for carbon, H for hydrogen to represent the constituent atoms, and electron dot notation to represent the valence shell electrons. Step 3: Sketch the Skeletal Diagram of the Molecule The central atom in an oxygen difluoride molecule is Oxygen. If we look at the Pauling Electronegativity chart, we can find out that the least electronegative element among oxygen and fluorine is Oxygen (O).
Now, we have to decipher the central atom in this molecule. Therefore, the total number of valence electrons = 6 + 7*2 = 20. Fluorine belongs to the family of halogen in group 17 and has a valency of 7. Oxygen belongs to group 16, the chalcogen family, and has a valency of 6. The first and foremost step is to calculate the total number of valence electrons in an OF2 molecule. Step 1: Find the Total number of Valence Electrons. Steps to form OF2 Lewis Structure Diagram Now, we will discuss the steps to form the Lewis Structure of OF2. It gives us a 2D figure and helps us have a brief idea about the electron arrangement and the type of bond formation without going much into detail.

Lewis Structure, thus, is a simple and constructive procedure to sketch a diagrammatic representation of a molecule with the help of electron-dot structures. Usually, the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, also known as valence electrons, take part in chemical bonding. When atoms come together and create bonds, a new molecule is created. Do you know that several factors make atoms come together and combine to form several different chemical compounds?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
